How to Calculate Reliability and Maintainability
In my recent post entitled IT Availability Management, (Facts & Fiction), I mention that I.T. availability management is made up of several elements including but not limited to Reliability and Maintainability. If you need to know how to measure Service Availability see How to Calculate Service Availability.
In this post we’ll walk through how to measure Reliability and Maintainability. My hope with this post is to equip I.T. managers with good practices for objectively reporting on the reliability and maintainability of the I.T. services they steward. This is also some handy information to have when you negotiate a service level agreement with a service provider.
I.T. Service Reliability
According to ITILv3 Reliability is defined as “A measure of how long a Configuration Item or IT Service can perform its agreed Function without interruption. Usually measured as Mean time between failures (MTBF) or Meantime between incidents (MTBSI.) The term Reliability can also be used to state how likely it is that a Process, Function, etc., will deliver its required outputs.
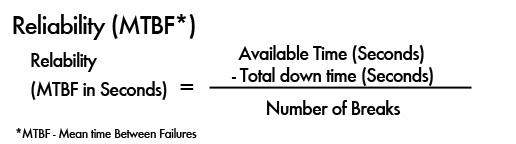
- Calculate Reliability (MTBF)
To calculate the reliability of a service in MTBF, your can subtract the total downtime from the available time in hours. You can then divide the result by the number of breaks.
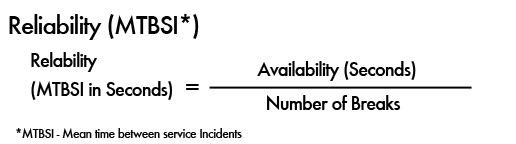
- Calculate Reliability (MTBSI)
To calculate the reliability of a service in MTBSI, you can divide the available time in hours by the number of breaks in service availability.
I.T. Service Maintainability
According to ITILv3, maintainability is defined as, “a measure of how quickly and Effectively a Configuration Item or IT Service can be restored to normal working after a Failure. Maintainability is often measured and reported as Meantime to restore service (MTRS).
- ITILv3 further states that, “Maintainability is also used in the context of Software or IT Service Development to mean ability to be Changed or Repaired easily.”
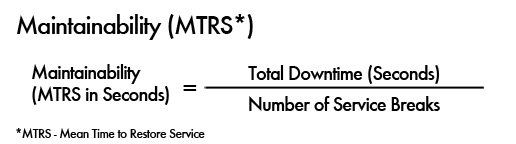
Calculate Maintainability
You can calculate the Meantime to Restore a service (MTRS), by dividing the total downtime in hours by the number of service breaks.
Related Posts